Do you know even a foreign citizen can be considered as a resident of India for Income Tax purposes or even an Indian citizen could be considered as a non-resident for Income Tax purpose?
The residential status as per Income Tax in India is a huge deciding factor for the taxability of an individual income.
The residential status of an individual can be classified as follow:

How do we determine the residential status?
The residential status of an individual depends on the duration of his stay in India.
1. Resident
A person is a resident of India, if he meets any of the following conditions:
(i) Stays in India for more than 182 days or more, or
(ii) Stays in India for 60 days or more in the relevant financial year and 365 days or more during 4 preceeding financial years.
Exceptions
In case a citizen of India leaves for employment outside India, the second condition mentioned above will not be applicable, and the person shall be considered as resident of India only if he stays for 182 days or more during the relevant financial year.
From FY 2020-21 onwards, in case a person is a citizen of India or a person of Indian origin, and his income from India exceeds Rs 15 lakh in any financial year, the period has been reduced to 120 days from 182 days.
From FY 2020-21 onwards, in case a person who is a citizen of India or a person of Indian origin comes to visit India and has income from India that exceeds Rs 15 lakh in any financial year, the time period in the second condition will be considered as 120 days instead of 60 days. In case, such person has income that does not exceed Rs 15 lakh, second condition will not be applied and only first condition will be applicable.
Income from foreign sources means income that accrues or arises out of India (except income derived from a business controlled in India or profession set up in India)
2. Non Resident
If a person does not satisfy any of the conditions mentioned in (i) and (ii) above, he is said to be a non-resident.
3. Ordinary and Not Ordinary Resident
If a person is qualified as a resident, the next step is to find out whether such person is an ordinary or not ordinary resident.
A person is a not ordinary resident, if he satisfies any one of these conditions:
1) He has been a non resident in 7 out of 10 preceeding financial years, or
2) He has been in India for less than 730 days in India in 7 preceeding financial years.
Satisfying any of the conditions above, the person will be said to be a non ordinary resident.
Satisying none of the consitions above, the person will be said to be resident and an ordinary resident.
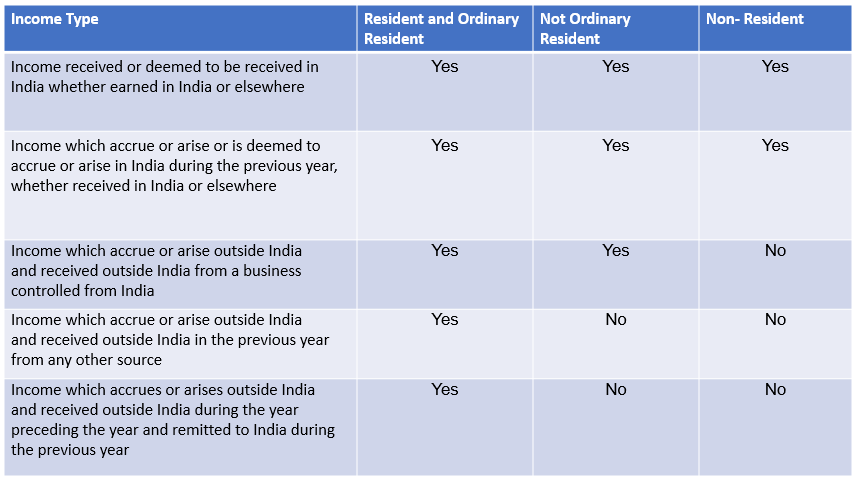
Taxability As Per Residential Status
Taxability of various residents is based on the form of income in the following manner:
Read about tax saving options for NRIs
